Recently, low, even dwarf, high-yielding varieties of fruit crops have become in high demand. This gives a number of advantages - it allows you to tighten plantings, ultimately increasing the yield per unit area, facilitates tree care, pruning and harvesting. Among the many varieties of common cherries listed in the State Register of selection achievements of the Russian Federation, small-fruited Shokoladnitsa cherries have recently become especially popular. In addition to the low height of the tree, the variety has a number of advantages compared to others, which contributes to its distribution in our gardens.
Description Cherries Chocolate
The variety was bred at the All-Russian Research Institute of Fruit Culture Selection in the Oryol Region and is recommended for use in the Central region of Russia. The chocolate girl was included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements in 1996.
According to the European classification, ordinary (non-felt, steppe, sand, decorative and Sakhalin) cherries are divided into two varieties:
- morel - varieties with dark red, almost black fruits in the stage of ripeness and coloring juice;
- amoreli - red varieties with colorless juice.
Shokoladnitsa refers to morel. Her varietal "parents" from which she was bred are Black and Lyubskaya consumer goods. This is a medium ripening cherry. The Shokoladnitsa begins to bear fruit 5 years after the beginning of the growth of an annual seedling, and the planted 1.5-2-year-old seedling gives a crop for the 3-4th year.
Grade advantages:
- small height - a fully developed adult tree does not exceed 2.5 m. When planting seedlings in large quantities, they are planted in the range of 2.5 m between the trunks and 3.5 m between the rows;

When planting cherries Chocolate variety observe an interval of 2.5 m between the trunks and 3.5 m between the rows
- compact crown - the main volume is located at the top, because the tree takes up little space, which makes the Chocolate Girl appropriate in small gardens;
- high productivity - suitable for cultivation both on an industrial scale and in small farms. A normally developed tree gives up to 15 kg of valuable berries;
- one of the most surviving varieties of cherries in frost and drought - these qualities were one of the main goals of breeders;
- sweeter berries than many other varieties of dark cherries - accumulate up to 12% sugar and about 1.5% acid;
- Significant life of the tree "at full capacity" - about 12 years. Chocolate Shelf Life - up to 17-20 years. But after 15 years, an aging tree is already beginning to noticeably reduce productivity;
- partially self-fertile variety - does not require mandatory cross-pollination with neighboring cherries during flowering.
The self-fertility of the variety means that a detached tree will bear fruit. However, many gardeners recommend planting Shokoladnitsa in a group with other varieties - the old variety Vladimirskaya (commonly known as Vladimirka), Turgenevskaya, Lyubskaya and others. It is believed that pollen transferred from variety to variety during flowering by insects improves the quality and increases the yield of a group of cherries of all varieties growing nearby. And at the same time there will be an opportunity to study and get the benefits of different varieties. An important point - when planting different varieties, you need to know their tallness and, if necessary, increase the distance between the trunks, so that then they do not obscure each other.
As for the shortcomings of the variety, in the reviews, gardeners call the great disadvantage of the Chocolate Girl the susceptibility to two diseases - coccomycosis and moniliosis. However, the description of the variety, given by the State Register of Breeding Achievements of the Russian Federation, refers to relative resistance to coccomycosis. Since there is no information about other deficiencies, it can be concluded that the lack of immunity to moniliosis is the only disadvantage of the variety. And it’s good enough to know the measures for the prevention and control of the disease in order to get rid of it.
Moniliosis appeared in Russia and the near abroad relatively recently: according to some sources, in the late 80s and early 90s. At that time, gardens first suffered in Belarus, then in our country.

Often, the causative agent of moniliosis penetrates the cherry stem during pruning, through fresh open slices
Often the infection penetrates the trunk during pruning, through fresh open slices. Therefore, the procedure is combined with spraying the crown with Bordeaux liquid or special antifungal drugs or proven folk remedies. For safety, the same treatment is repeated after flowering.
Spores hibernate under a tree in fallen foliage. Therefore, the preventive measure of moniliosis is to rake and burn all the fallen leaves in the autumn, sprinkle the soil with quicklime, fluff and add a new mulch to the trunk circle for the winter to protect the roots from freezing. And also it is impossible to leave dried or decayed fruits on the tree - they can become nurseries for many pests.
A normally developed, well-lit, non-dense, blown tree without stagnant dampness in the crown has strong immunity and can better resist any disease.
Planting Cherries Chocolate
When landing, you must follow some rules.
Seat selection
The chocolate girl will develop well in a lighted, not swampy place, preferably without drafts. It is relatively shade-tolerant, but in a strong shadow the tree will grow more slowly, the berries will grow small and acidic, and because of the dampness without the sun, the risk of diseases is noticeably higher.
There are places where cherries cannot grow in principle due to the high level of groundwater - closer than 1.5 m from the surface. As soon as the roots of a growing tree reach this depth, the tree dies. And this may not happen immediately, but a few years after planting - on the 4-6th year, the roots can reach a depth of 1.6 m.

Shokoladnitsa cherries will develop well in an illuminated place with a low level of groundwater
Soil preparation
Cherry of this variety is not too demanding on the quality of the soil, but there are two positions that must be observed:
- neutral or slightly alkaline soil with a pH of 7.0;
- the soil is loose, breathable and without stagnant water.
On loamy, clay-free clay loam, the roots of the cherry will suffocate and rot. To plant on such soils, a large amount of earthwork is required:
- The landing pit should be prepared not by the size of the root system of the seedling, but many times wider and deeper. The thin root system of the cherry is located at a depth of 15 to 70 cm (the bulk is at a depth of 20-40 cm). Thick, tree-like roots can go to great depths, but you do not need to prepare soil under them, they can develop in any breed. By area, the roots of cherries can be several times the size of the crown, so under one bush you will have to change the soil on a circle with a diameter of at least 3 m from the trunk:
- to a depth of 40-50 cm away from the center;
- to a depth of 70 cm in the center, on the site of direct landing.

On heavy soils, a landing pit for cherries is prepared much larger in size than on loose
- The selected soil must be mixed with turf soil, chernozem, humus, peat until it becomes sufficiently loose.
- Thus, the prepared soil is returned to the place and further landing is as usual.
The method is laborious, for planting a large number of trunks it is better to find another site.
Seedling selection and planting
Most often they use one and a half year old seedlings up to 60-80 cm high with a well-developed root system (seedlings of this age take root well). But there are also recommendations to plant 2-3-year-old seedlings in order to get the first crop faster for 1-2 years. Landing is carried out during the rest period - in the fall in October or in the spring in the beginning of April. It is done like this:
- Dig a landing hole in the size of the roots in a straightened form. As a rule, for 1.5-year-olds it is 40 cm in diameter and about 80 cm in depth.
- The soil selected from the pit is mixed with humus (about 3 liters per 10 liters of soil) and wood ash - 0.5 liters per 10 liters of soil.
- In the center they drive in a count.

A young cherry seedling must be tied to a stake to protect it from strong winds
- Soil is poured into a pit with a knoll 15-20 cm high.
- A sapling is lowered onto the knoll, carefully spreading the roots. Planted at the same depth at which the seedling grew in the nursery, which is clearly visible by the color of the bark. But the root neck should not be bombarded. If it is much lower than the ground level, the sapling is raised and poured mound higher. The optimal height of the root neck above the ground is 3-5 cm.

The root neck of a cherry seedling should be 3-5 cm above the soil
- The roots are poured with loose soil so that there are no large air voids.
- Compact the soil around the trunk.
- Watered at the rate of 10 liters of water per 1 barrel.
- The seedling is tied to a stake with a cord not traumatic to the bark or a strip of soft tissue.
- Mulch with humus, peat, rotten sawdust or grass cut with a layer of about 5 cm.

After planting and watering, the seedlings are mulched with a layer of at least 5 cm
Chocolate Care
Further care in the first year for the seedling is simple:
- it is necessary to ensure that the near-stem circle is clean of weeds;
- in the absence of heavy rains in late May - early June, the seedling will need to be watered 10-15 liters of water. Further during the summer and autumn, watering may be required only in case of abnormal drought.
Pruning
In the future, Shokoladnitsa cherry will need pruning, which is carried out in early spring before the start of sap flow. Cherry must be cut carefully and precisely: this is not the sort of variety that grows up to 7 m and has a powerful branched crown, where the plus or minus of the branch is of little importance. A chocolate bar cannot be trimmed just for cropping and crown formation. Types and purposes of trimming:
- sanitary - remove all sick, broken, withered branches. The entire root shoot is cut below - it only weakens the tree;
- forming cropping:
- if irregular branches have grown - growing inside the crown, to the ground, intertwined, then they are removed. The branch is cut "into a ring", that is, without hemp. The place of the cut is covered with garden varnish, because if the pruning is incorrect, a hollow may form in the place of the cut over time, the tree will rot, become sick and may die;
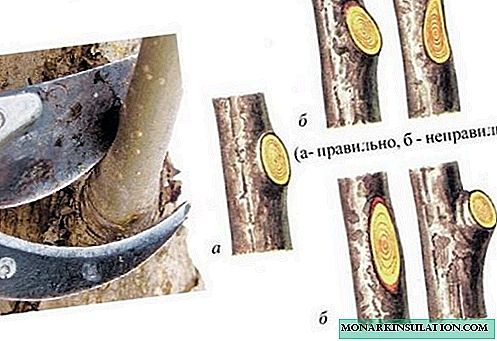
It is important to cut the branches of cherry correctly so that the focus of the disease does not form at the site of the cut
- thin out the skeletal branches so that between them there is at least 10-15 cm to eliminate thickening. An adult tree should have 10-15 main skeletal branches;
- if irregular branches have grown - growing inside the crown, to the ground, intertwined, then they are removed. The branch is cut "into a ring", that is, without hemp. The place of the cut is covered with garden varnish, because if the pruning is incorrect, a hollow may form in the place of the cut over time, the tree will rot, become sick and may die;
- anti-aging - carried out if an adult tree is bare - at the ends of the branches there is no foliage and buds - and poorly bears fruit. About a third of all the main branches are shortened by about 1 m. In summer, numerous young shoots will appear on the site of the sections.
The main thing you need to know is that cherry gives fruits almost exclusively on the young growth of the previous year. This is a single or bunch of big-leafed branches with lots of buds. And if you cut them all off, there will simply be no harvest. Therefore, the main pruning is done in the spring in order to stimulate the active growth of young shoots in the summer, which will give a plentiful harvest for next year.
And also in the spring you can cut the fruiting branches last year - this year there will be no harvest on them. Their ends are cut into several buds, in no case touching the last year's replacement shoots, which will bear fruit this year. And at the place of the cut, several young shoots may appear that will bear fruit for next year.
Cherry is very sensitive to incorrect and too strong pruning. She has a small annual growth, and after each pruning she does not recover quickly. Therefore, the principle “it’s better not to trim than to trim the excess” is suitable here.
Reviews
The chocolate maker is self-fertile, which is a plus, of course. But the taste of cherries themselves is not perfect, and even a big minus, IMHO, it is susceptible to the main cherry sores - coccomycosis and moniliosis. I tried to plant it, but the sapling (was with ACS) did not begin and, having suffered during the summer, died. It was replaced by Kharitonovskaya, which is tastier and more resistant to fungal sores.
mooch
//forum.auto.ru/garden/37453/
The fruits are cool, but we get very little. Blackbirds eat everything. The grid must be closed. And care is like any cherry.
water meter (s)
//forum.auto.ru/garden/37453/
I still have a small tree, the first time it bore fruit. But close to him, the pollinator seems to be not noticed. The nearest is a neighbor’s felt cherry, but she doesn’t pollinate an ordinary cherry. So, either self-fertile or the second young cherry next to the Chocolate Girl blossomed unnoticed.
Starche-05
//forum.auto.ru/garden/37453/
The taste of cherries has been familiar to everyone since childhood, and Russian gardens are inconceivable without this tree. Among the many varieties, Shokoladnitsa looks like a very worthy option with good frost resistance and drought tolerance, as well as the sweetest taste of berries among black varieties. Alone or in a group, this variety, of course, can be of great benefit to its owners.

















